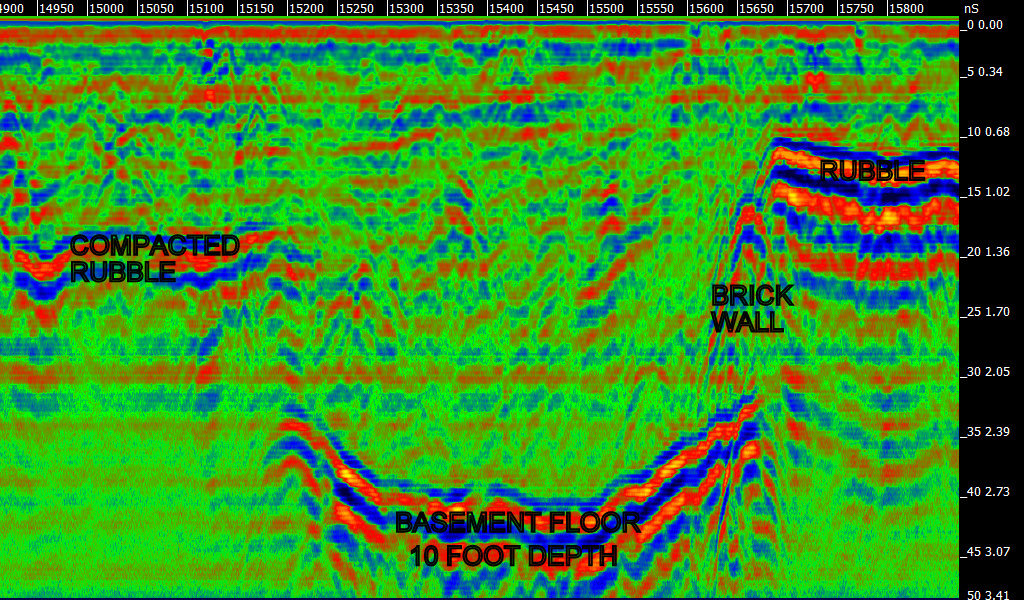
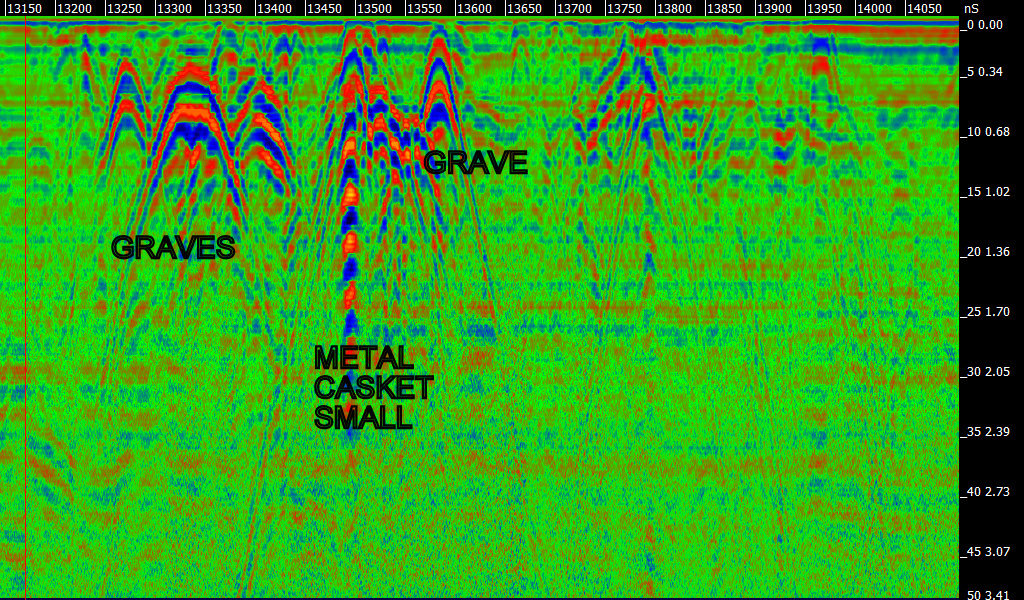
Utility
Ground-penetrating radar is a reliable solution for locating underground utilities. Standard electromagnetic induction utility locating tools, require utilities to be conductive. These tools are ineffective for locating plastic conduits or concrete storm and sanitary sewers. Since GPR detects variations in dielectric properties in the subsurface, it usefull for locating non-conductive utilities.